Daniel Van Heil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Daniel van Heil or Daniël van HeilDaniel van Heil
at the
at Christie’s
 It is not known with whom Daniel trained but it was likely his father. He became a master in the Brussels
It is not known with whom Daniel trained but it was likely his father. He became a master in the Brussels
at Christie’s His son Theodoor van Heil trained with his father and produced landscapes of similar subject matter executed in the same style as his father. The artist died in Brussels in 1664.
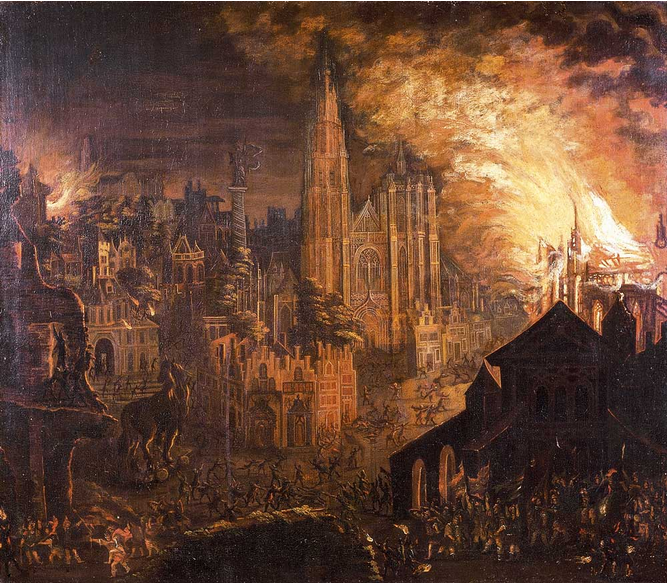 The theme of the fall of Troy and the flight of Aeneas with his father was a subject to which van Heil often returned. In his scenes of Troy the artist also presented an anachronistic vision of the city by combining Antique ruins with contemporary buildings. This is demonstrated in the ''Burning of Troy'' (at Christie's New York on 26 January 2005, lot 214) in which classical structures are found next to church spires and basilicas in the background and more humble typically Flemish houses in the foreground. By emphasizing the magnificence of the diverse structures van Heil linked Brussels as the residence of the Archduke and Archduchess Albert and Isabella with Troy as the court residence of King Priam. The architecture dominates the composition and the protagonists of the battle only appear as miniature figures. The intense human tragedy of the scene is expressed through the menacing sky which takes up a large portion of the canvas in vertical format which was unusual for the artist.
Daniel van Heil's winter landscapes were in the tradition of Breughel the Elder, with a tendency towards pre-Romantic Impressionism.Leo van Puyvelde, Thierry van Puyvelde, ''Flemish painting, the age of Rubens and Van Dyck'', McGraw-Hill, 1971, 198 His winter views show the influence of the Ruisdaels as well as other artists such as Kerstiaen de Keuninck, especially in his early works. From these artists he took the compositional scheme. A characteristic motif of his landscapes is the presence of naked trees lit from behind with the interlacing branches framing the scene.Daniel van Heil
The theme of the fall of Troy and the flight of Aeneas with his father was a subject to which van Heil often returned. In his scenes of Troy the artist also presented an anachronistic vision of the city by combining Antique ruins with contemporary buildings. This is demonstrated in the ''Burning of Troy'' (at Christie's New York on 26 January 2005, lot 214) in which classical structures are found next to church spires and basilicas in the background and more humble typically Flemish houses in the foreground. By emphasizing the magnificence of the diverse structures van Heil linked Brussels as the residence of the Archduke and Archduchess Albert and Isabella with Troy as the court residence of King Priam. The architecture dominates the composition and the protagonists of the battle only appear as miniature figures. The intense human tragedy of the scene is expressed through the menacing sky which takes up a large portion of the canvas in vertical format which was unusual for the artist.
Daniel van Heil's winter landscapes were in the tradition of Breughel the Elder, with a tendency towards pre-Romantic Impressionism.Leo van Puyvelde, Thierry van Puyvelde, ''Flemish painting, the age of Rubens and Van Dyck'', McGraw-Hill, 1971, 198 His winter views show the influence of the Ruisdaels as well as other artists such as Kerstiaen de Keuninck, especially in his early works. From these artists he took the compositional scheme. A characteristic motif of his landscapes is the presence of naked trees lit from behind with the interlacing branches framing the scene.Daniel van Heil
at the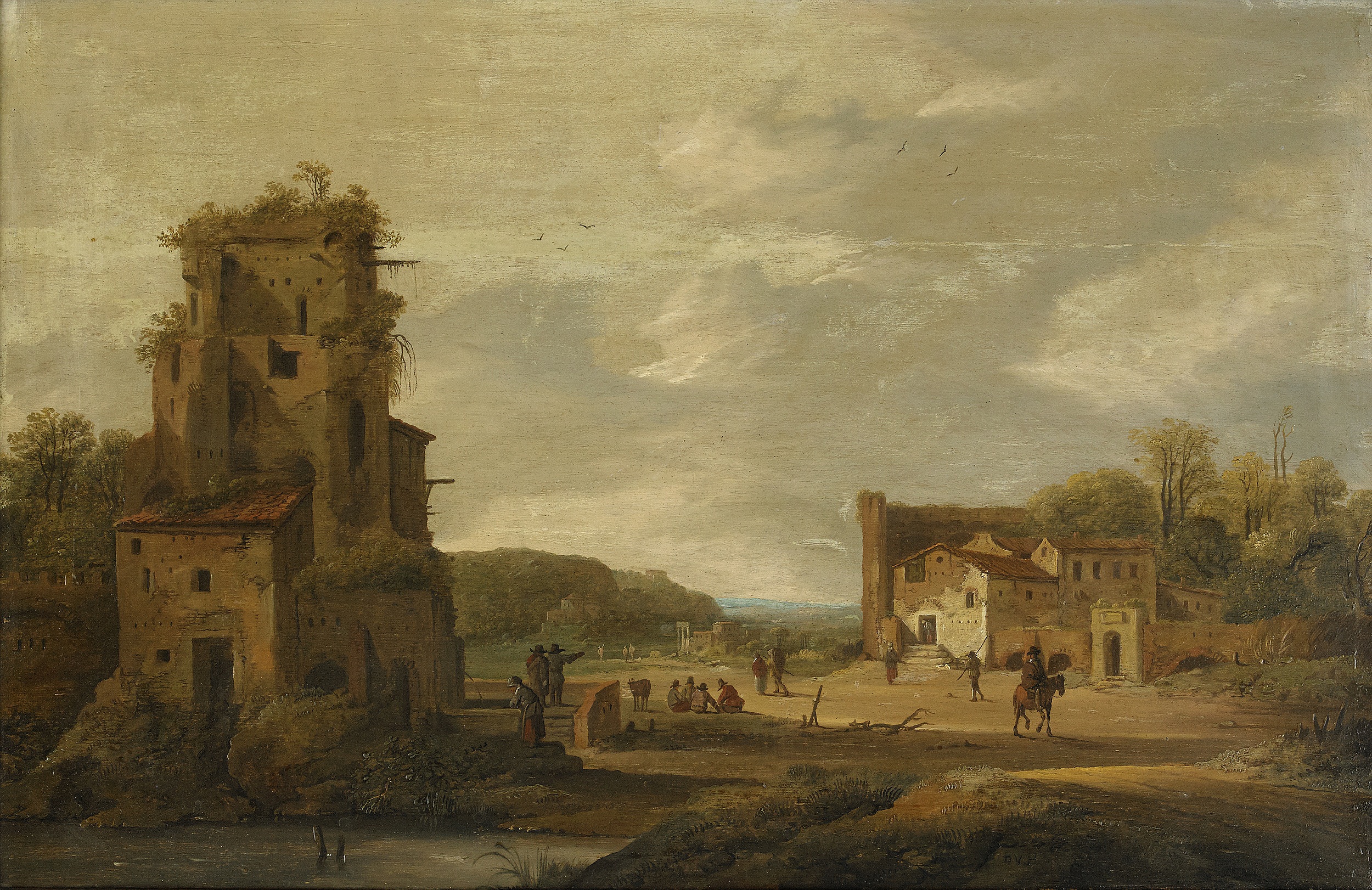 Daniel van Heil collaborated with his brother Jan Baptist on the ''Infante Isabella in the gardens of the Coudenberg Palace'' (c. 1630,
Daniel van Heil collaborated with his brother Jan Baptist on the ''Infante Isabella in the gardens of the Coudenberg Palace'' (c. 1630, Bezoek aan de archeologische site van het voormalige paleis van Brussel op de Coudenberg
at the
Netherlands Institute for Art History
The Netherlands Institute for Art History or RKD (Dutch: RKD-Nederlands Instituut voor Kunstgeschiedenis), previously Rijksbureau voor Kunsthistorische Documentatie (RKD), is located in The Hague and is home to the largest art history center i ...
(Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, 1604 – Brussels, 1664) was a Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
landscape painter. He specialised in three types of landscapes: scenes with fire, landscapes with ruins and winter landscapes.Daniel van Heil, ''The Burning of Troy''at Christie’s
Life
Little is known about the life and training of Daniel van Heil. He was born in Brussels. His father Leo or Leon was a painter and two of his brothers were also artists: Leo was an architect and painter and Jan Baptist was a portrait painter. It is not known with whom Daniel trained but it was likely his father. He became a master in the Brussels
It is not known with whom Daniel trained but it was likely his father. He became a master in the Brussels Guild of St. Luke
The Guild of Saint Luke was the most common name for a city guild for painters and other artists in early modern Europe, especially in the Low Countries. They were named in honor of the Four Evangelists, Evangelist Saint Luke, Luke, the patron sa ...
in 1627.Daniel van Heil, ''A fire in Brussels at night''at Christie’s His son Theodoor van Heil trained with his father and produced landscapes of similar subject matter executed in the same style as his father. The artist died in Brussels in 1664.
Work
Daniel van Heil was a landscape painter. His subjects were principally winter landscapes, fires in cities and landscapes with ruins. The theme of fires in cities, which appeared in the early 17th century was not new to Flemish iconography. The subject often appeared in earlier art as a secondary theme in depictions of biblical or mythological apocalypses and destruction. These earlier works often set the subject at night in an environment sometimes populated with fantastic or demonic beings. The actual subjects of these scenes included the fall of Troy,Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas (, ; from ) was a Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy (both being grandsons ...
and Juno
Juno commonly refers to:
*Juno (mythology), the Roman goddess of marriage and queen of the gods
*Juno (film), ''Juno'' (film), 2007
Juno may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
*Juno, in the film ''Jenny, Juno''
*Ju ...
in the underworld and the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah. Hieronymus Bosch was the first northern artist to paint such fire scenes and later painters in the Brueghel dynasty developed the subject matter further.
In the 17th century the theme of fires in cities became an independent subject matter in its own right. The subject was explored mainly for its formal aspects and pictorial possibilities: the depiction of spectacular effects of light and shadow had become a goal in itself. A simultaneous development was for the subjects of the compositions to become less clear and elements of tradition and innovation to become mixed. This is reflected in the architectural setting of the scenes, where contemporary architecture forms the background for a mythological or biblical scene.''Le peintre et l'arpenteur: images de Bruxelles et de l'ancien duché de Brabant'', Musées royaux des beaux-arts de Belgique Renaissance Du Livre, 2000, pp. 99–100 This mixing up of myth and contemporary events was possibly a result of the experiences of the artist who lived in a time when war and destruction of cities by armies was not uncommon. These works thus used the iconic examples of classical antiquity to give voice to their indignation about contemporary destructions they had witnessed.
This is illustrated by van Heil's ''Fire of Antwerp with the Trojan horse''. This composition shows the mixing of contemporary events such as the sack of Antwerp by Spanish troops in 1576 known as the Spanish Fury
A Spanish Fury (or the Spanish Terror) was one of a number of violent sackings of cities in the Low Countries, mostly by Spanish Habsburg armies, that occurred in the years 1572–1579 during the Dutch Revolt. In some cases the sack did not fol ...
, with mythological elements such as the Trojan horse. It is also not entirely clear whether the city depicted is in fact Antwerp. The church represented in the centre bears a resemblance to Antwerp Cathedral
The Cathedral of Our Lady ( nl, Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal) is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Antwerp, Belgium. Today's see of the Diocese of Antwerp started in 1352 and, although the first stage of construction was ended in 1521, has never been ...
but the city architecture further includes Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
of Rome. Some of the buildings depicted may actually be buildings in Brussels. This mixing of real and fantastic elements in the work reinforces the impression that the city it represents is imaginary.
at the
Prado Museum
The Prado Museum ( ; ), officially known as Museo Nacional del Prado, is the main Spanish national art museum, located in central Madrid. It is widely considered to house one of the world's finest collections of European art, dating from the ...
His landscapes with ruins were in the style of Netherlandish Italianate landscapers.
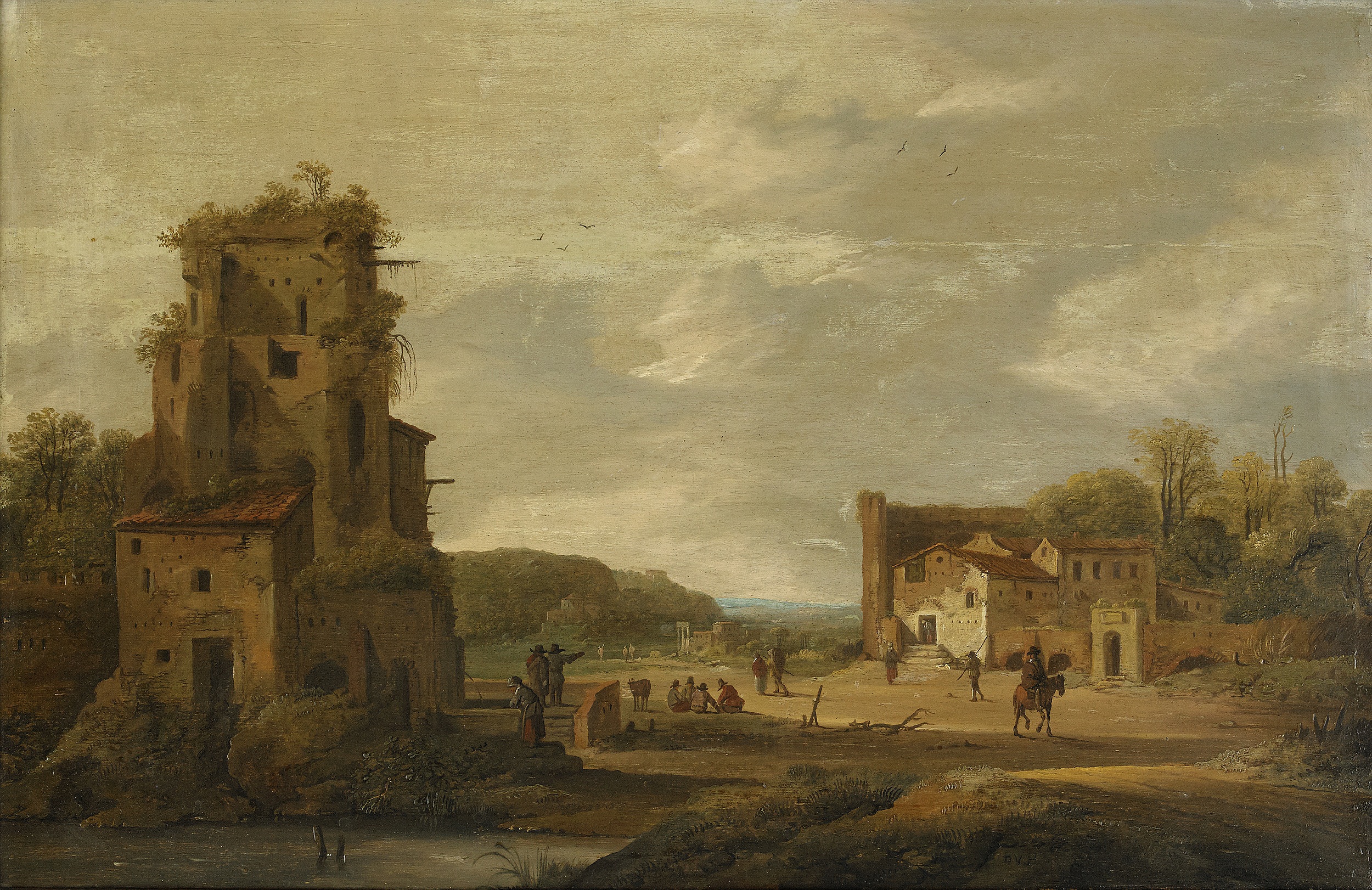 Daniel van Heil collaborated with his brother Jan Baptist on the ''Infante Isabella in the gardens of the Coudenberg Palace'' (c. 1630,
Daniel van Heil collaborated with his brother Jan Baptist on the ''Infante Isabella in the gardens of the Coudenberg Palace'' (c. 1630, Museum of the City of Brussels
The Brussels City Museum (french: Musée de la ville de Bruxelles, nl, Museum van de Stad Brussel) is a municipal museum on the Grand-Place/Grote Markt of Brussels, Belgium. Conceived in 1860 and inaugurated in 1887, it is dedicated to the hi ...
). Daniel is believed to have been responsible for the landscape with the palace while his brother Jan Baptist for the staffage
In painting, staffage () are the human and animal figures depicted in a scene, especially a landscape, that are not the primary subject matter of the work. Typically they are small, and there to add an indication of scale and add interest.
Before ...
. The canvas shows a landscape with the palace of the governors of the Southern Netherlands near Brussels. In the foreground the Archduchess Isabella, widow of Archduke Albrecht and reigning governess, walks in the gardens of the palace in the habit of the Poor Clares
The Poor Clares, officially the Order of Saint Clare ( la, Ordo sanctae Clarae) – originally referred to as the Order of Poor Ladies, and later the Clarisses, the Minoresses, the Franciscan Clarist Order, and the Second Order of Saint Francis ...
, a religious order the Archduchess had joined after the death of her husband.References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Heil, Daniel van 1604 births 1664 deaths Flemish Baroque painters Flemish landscape painters Artists from Brussels Painters from Brussels